Test splitting and parallelism
On This Page
Use parallelism and test splitting to:
- Reduce the time taken for the testing portion of your CI/CD pipeline.
- Specify a number of executors across which to split your tests.
- Split your test suite using one of the options provided by the CircleCI CLI: by name, size or by using timing data.
If you are interested to read about concurrent job runs, see the Concurrency overview page.
Introduction
Pipelines are often configured so that a set of tests are run each time code is committed. The more tests your project has, the longer it will take for them to complete using a single compute resource. To reduce this time, you can split your tests and run them across multiple, parallel-running execution environments. Test splitting is a great way to speed up the testing portion of your CI/CD pipeline.
CircleCI test splitting lets you intelligently define where splits happen across a test suite:
- By name
- By size
- Using timing data
It is also possible to use the CLI to manually allocate tests across parallel environments. Another alternative is to use environment variables instead of the CLI to configure split tests.
Quickstart
The following how-to guide walks you through the steps required to glob your test files, split your tests evenly across parallel containers or VMs, and then run your tests in parallel:
Specify parallel environments for a test job
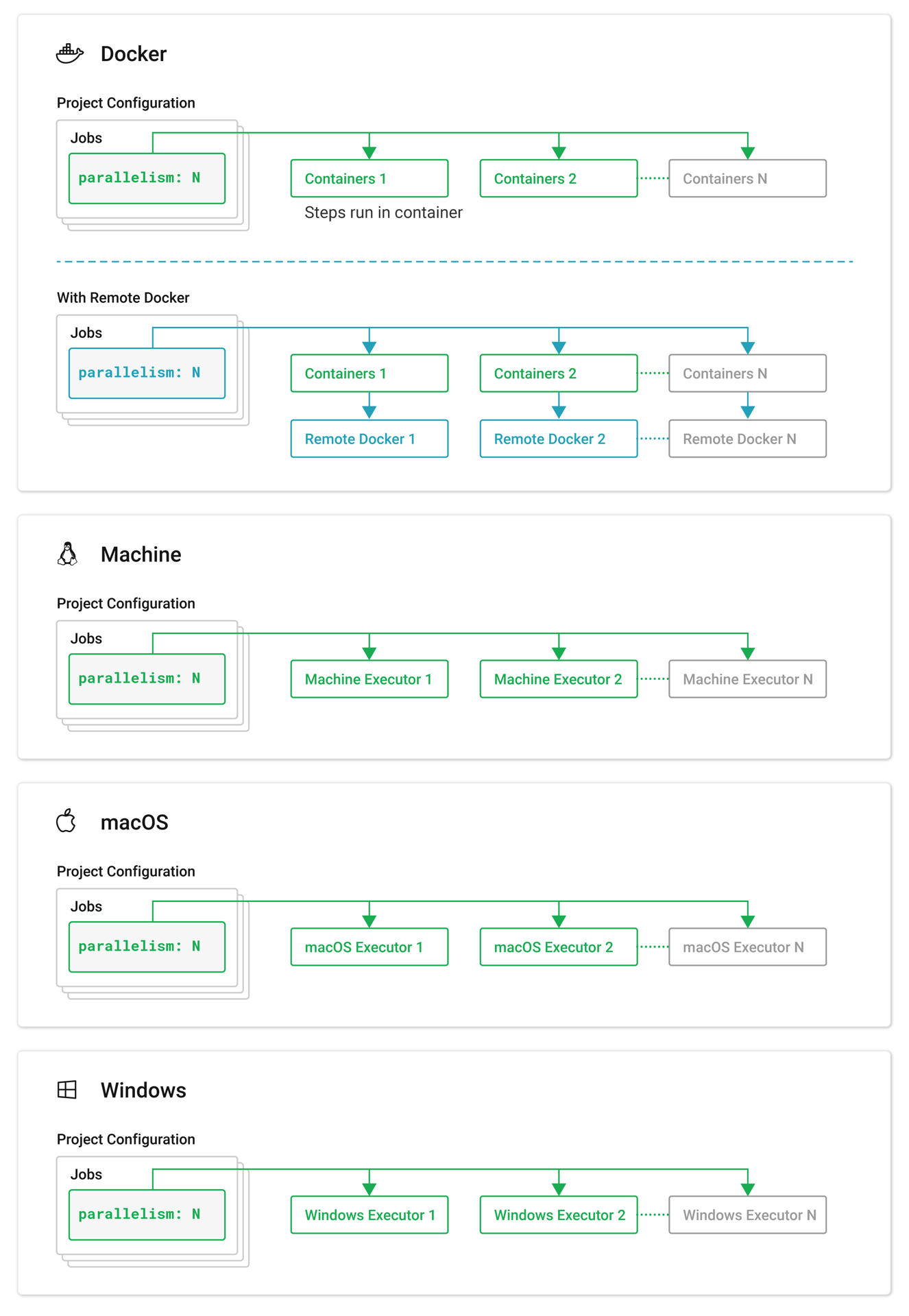
Test suites are conventionally defined at the job level in your .circleci/config.yml file. The parallelism key specifies how many independent executors are set up to run the job.
To run a job’s steps in multiple, parallel execution environments, set the parallelism key to a value greater than 1. In the example below, parallelism is set to 4, meaning four identical execution environments will be set up for the job, in this case, four Docker containers using the cimg/base:2023.09 image.
Use the circleci tests run command to split and run your tests. Your tests will be split up, and a portion of your tests run in each execution environment. This reduces the overall time taken to run the full test suite. In this example tests will be split up into four, and the split points are calculated based on historic timing data.
# ~/.circleci/config.yml
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: cimg/go:1.18.1
parallelism: 4
resource_class: large
steps:
- run: go list ./... | circleci tests run --command "xargs gotestsum --junitfile junit.xml --format testname --" --split-by=timings --timings-type=name
Use parallelism with self-hosted runners
To use the parallelism feature with jobs that use self-hosted runners, ensure that you have at least two self-hosted machine runners associated with the runner resource class that your job will run on. If you set the parallelism value to be greater than the number of active self-hosted runners in a given resource class, the excess parallel tasks that do not have a self-hosted runner on which to execute will queue until a self-hosted runner is available.
If you are using parallelism on Container Runner, you will need to make sure that agent.maxConcurrentTasks and your Kubernetes cluster can accommodate the number of parallel tasks you want to run. If you do not have adequate resources, your parallel runs will be subject to queuing.
For more information, see the Configuration reference page.
How test splitting works
CircleCI’s test splitting feature allows you to specify a number of identical execution environments for a job (parallelism), and then split your test suite into an equal number of portions so that the tests can be run in parallel to reduce the length of time taken for your test pipeline. You can split your tests up in a few different ways:
- Alphabetically, by name. This is the default:
# ~/.circleci/config.yml jobs: build: docker: - image: cimg/go:1.18.1 parallelism: 4 resource_class: large steps: - run: go list ./... | circleci tests run --command "xargs gotestsum --junitfile junit.xml --format testname --" - By size:
# ~/.circleci/config.yml jobs: build: docker: - image: cimg/go:1.18.1 parallelism: 4 resource_class: large steps: - run: go list ./... | circleci tests run --command "xargs gotestsum --junitfile junit.xml --format testname -- --split-by=filesize" - By using historic timing data:
jobs: build: docker: - image: cimg/go:1.18.1 parallelism: 4 resource_class: large steps: - run: go list ./... | circleci tests run --command "xargs gotestsum --junitfile junit.xml --format testname --" --split-by=timings --timings-type=name
When using timing-based test splitting, the CLI attempts to auto detect the granularity of the test split (for example, whether to split by file name, or down to class name) based on the input to the split command. You may need to choose a different timing type depending on how your test coverage output is formatted, using the --timings-type option. Valid timing types are:
name- test nameclassnameclass namefile- file name
Example using timing-based test splitting
Using timing-based test splitting as an example, timing data from the previous test run is used to split a test suite as evenly as possible over a specified number of test environments running in parallel. This delivers the lowest possible test time for the compute power in use.
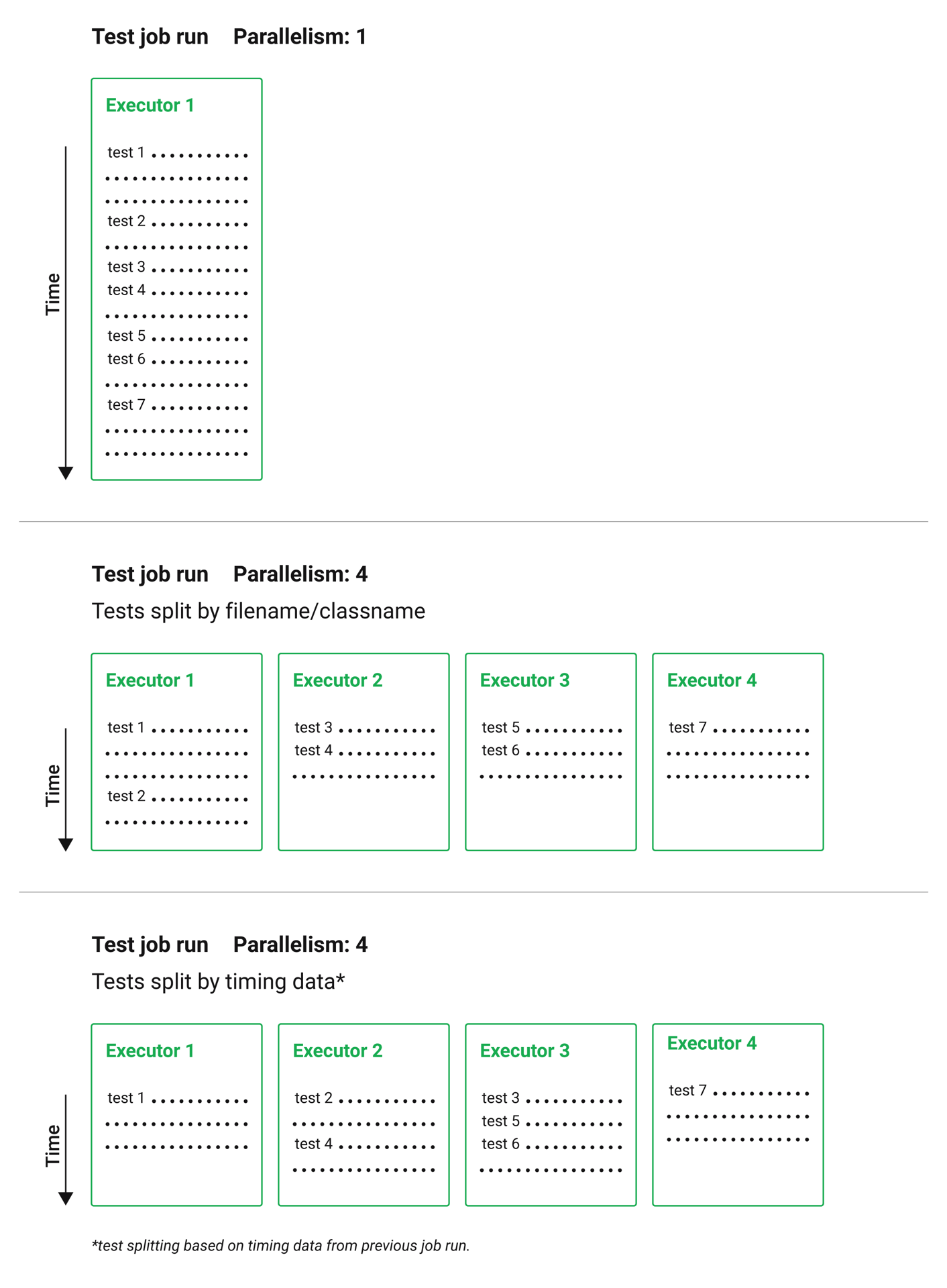
Timings-based test splitting gives the most accurate split, and is guaranteed to optimize with each test suite run. The most recent timings data is always used to define where splits are made.
As an example, take a Go test suite. Here, all tests run sequentially in a single test environment, a Docker container:
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: cimg/go:1.18.1
resource_class: large
steps:
- run: go test
To split these tests using timing data:
- Introduce parallelism to spin up a number of identical test environments (4 in this example)
- Use the
circleci tests runcommand, with the--split-by=timingsflag to split the tests evenly across all executors.
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: cimg/go:1.18.1
parallelism: 4
resource_class: large
steps:
- run: go list ./... | circleci tests run --command "xargs gotestsum --junitfile junit.xml --format testname --" --split-by=timings --timings-type=name
For a more detailed walkthrough, read the guide to using the CLI to split tests, or follow our Test splitting tutorial.
The tests run command
Use the circleci tests run command to run your tests, split your tests across parallel executors and take advantage of the rerun failed tests options.
The following table show a full list of option flags available when using circleci tests run.
| Flag | Type | Description | Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
--command | string | The command string is the script that will be run for a list of tests determined by the options provided to the plugin | Yes |
--index | uint | index of node can also be set with CIRCLE_NODE_INDEX. (default 1) | No |
--split-by | string | how to weight the split, allowed values are “name”, “filesize”, and “timings”. (default “name”) | No |
--timings-type | string | name of the field to use from historical test results when matching against the test names given to the command in order to determine their historical timings, previous status and flakiness. Available values: classname, name, file (default). | No |
--total | uint | number of nodes can also be set with CIRCLE_NODE_TOTAL. (default 2) | No |
-v, --verbose | — | enable verbose logging output. | No |
The tests split command
It is also possible to split tests using the circleci tests split command. Using the example from above, splitting the Go tests would be done as follows:
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: cimg/go:1.18.1
parallelism: 4
resource_class: large
steps:
- run: go test -v $(go list ./... | circleci tests split --split-by=timings)
The circleci tests split command has been superceded by circleci tests run as this command also gives you access to the rerun failed tests options.
Integrating with some third party tools might still require you to use circleci tests split. For usage steps see, Use the CircleCI CLI to split tests.
JUnit XML report formatting
In order to use the test splitting feature, CircleCI requires test results to be uploaded as JUnit XML reports. The following formatting allows CircleCI to parse timing data from test results and use the data for test splitting:
- The
fileattribute, either on the<testsuite>or<testcase>tag - The
timeattribute, on the<testcase>tag
The following example is a snippet from an XML file with a format that CircleCI can parse:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<testsuites name="Mocha Tests" tests="3" failures="1">
<testsuite tests="3">
<testcase classname="foo1" name="ASuccessfulTest" time="10" file="src/__tests__/App.test.js" />
<testcase classname="foo2" name="AnotherSuccessfulTest" time="5" file="src/__tests__/App.test.js" />
<testcase classname="foo3" name="AFailingTest" time="1.1050" file="src/__tests__/App.test.js">
<failure type="NotEnoughFoo"> details about failure </failure>
</testcase>
</testsuite>
</testsuites>
Manual allocation
For full control over how tests are split across parallel executors, CircleCI provides two environment variables that you can use in place of the CLI to configure each container individually.
$CIRCLE_NODE_TOTALis the total number of parallel containers being used to run your job.$CIRCLE_NODE_INDEXis the index of the specific container that is currently running.
The CLI looks up the number of available execution environments ($CIRCLE_NODE_TOTAL), along with the current container index ($CIRCLE_NODE_INDEX). Then, it uses deterministic splitting algorithms to split the test files across all available containers.
The number of containers is specified by the parallelism key in the project configuration file.
The current container index is automatically picked up from the $CIRCLE_NODE_INDEX environment variable, but can be manually set by using the --index flag.
cat test_filenames.txt | circleci tests run --command=">index0.txt xargs echo" --index=0 --split-by=name
Refer to the Project values and variables page for more details.
Other ways to split tests
Some third party applications and libraries might help you to split your test suite. These applications are not developed or supported by CircleCI. Please check with the owner if you have issues using it with CircleCI. If you are unable to resolve the issue you can search and ask on our forum, Discuss.
-
Knapsack Pro - Enables allocating tests dynamically across parallel CI nodes, allowing your test suite execution to run faster. See CI build time graph examples.
- phpunit-finder - This is a helper CLI tool that queries
phpunit.xmlfiles to get a list of test filenames and print them. This is useful if you want to split tests to run them in parallel based on timings on CI tools. -
go list - Use the built-in Go command
go list ./...to glob Golang packages. This allows splitting package tests across multiple containers.go test -v $(go list ./... | circleci tests split) -
Playwright - This is a framework for web testing and automation and allows running sharded tests out of the box. For more details see playwright docs.
job-name: executor: pw-focal-development parallelism: 4 steps: - run: SHARD="$((${CIRCLE_NODE_INDEX}+1))"; npx playwright test --shard=${SHARD}/${CIRCLE_NODE_TOTAL}