Deploy to Amazon SageMaker
This how-to guide walks you through the steps to set up and use the Amazon SageMaker orb to deploy and release models to SageMaker. It uses the sample repository example project repository as a reference, but you can adapt every step to your requirements. Through this guide, you will learn how to orchestrate model deployment to endpoints across different environments, as well as track and manage your deployments in the CircleCI deploys UI.
For further information about the orb and the CircleCI deploys feature see the following:
Prerequisites
To follow along with this how-to guide you will need the following:
-
A CircleCI account connected to your code. You can sign up for free
-
Basic knowledge of Amazon SageMaker
-
An AWS account with access to SageMaker
-
A SageMaker studio domain to follow along the training step, or an existing Model Package Registry if you have already trained one
-
A copy of the example repository building on CircleCI. For steps to get the project set up, see the Create a project in CircleCI page.
1. Set up a CircleCI environment integration
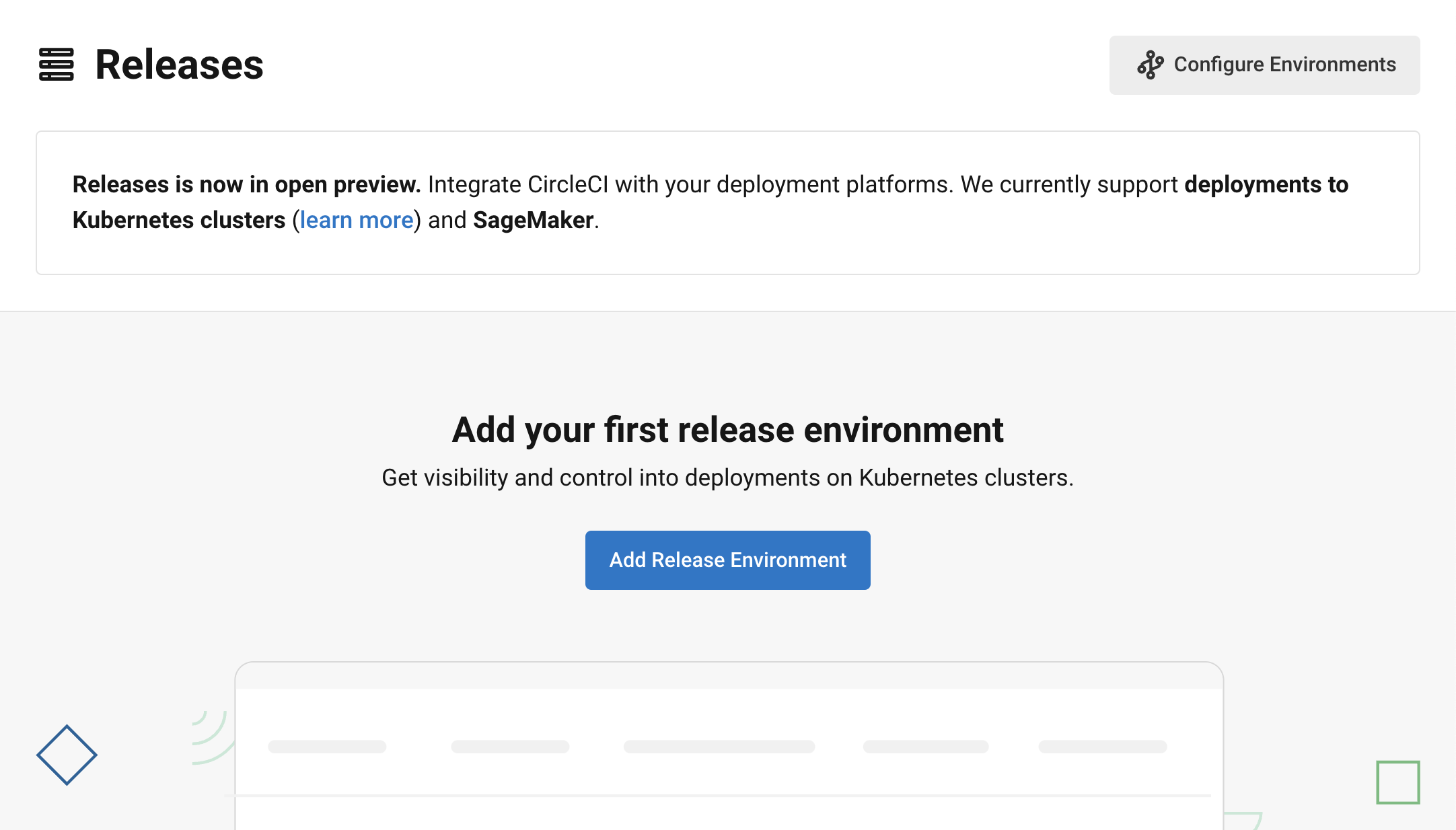
First, set up an environment integration to monitor your deployments from the CircleCI web app, and access options to manage promotions and rollbacks.
-
In the CircleCI web app, select Deploys from the sidebar
-
If this is your first environment integration, you will see an option to Create your first environment integration. If not, select the "Environments" tab, and then select Create Environment Integration
-
In the popup, select Amazon SageMaker from the "Type" dropdown. Follow the instructions on screen to generate and save a token.
2. Set up Amazon SageMaker access
a. OIDC Identity Provider
In this section you will create an IAM (Identity and Access Management) Identity Provider in your AWS IAM for the CircleCI OIDC Provider. The Amazon SageMaker orb uses OIDC. You may already have this set up, in which case you can skip this section. For more information on CircleCI OIDC functionality, see the Using OpenID Connect tokens in jobs page.
-
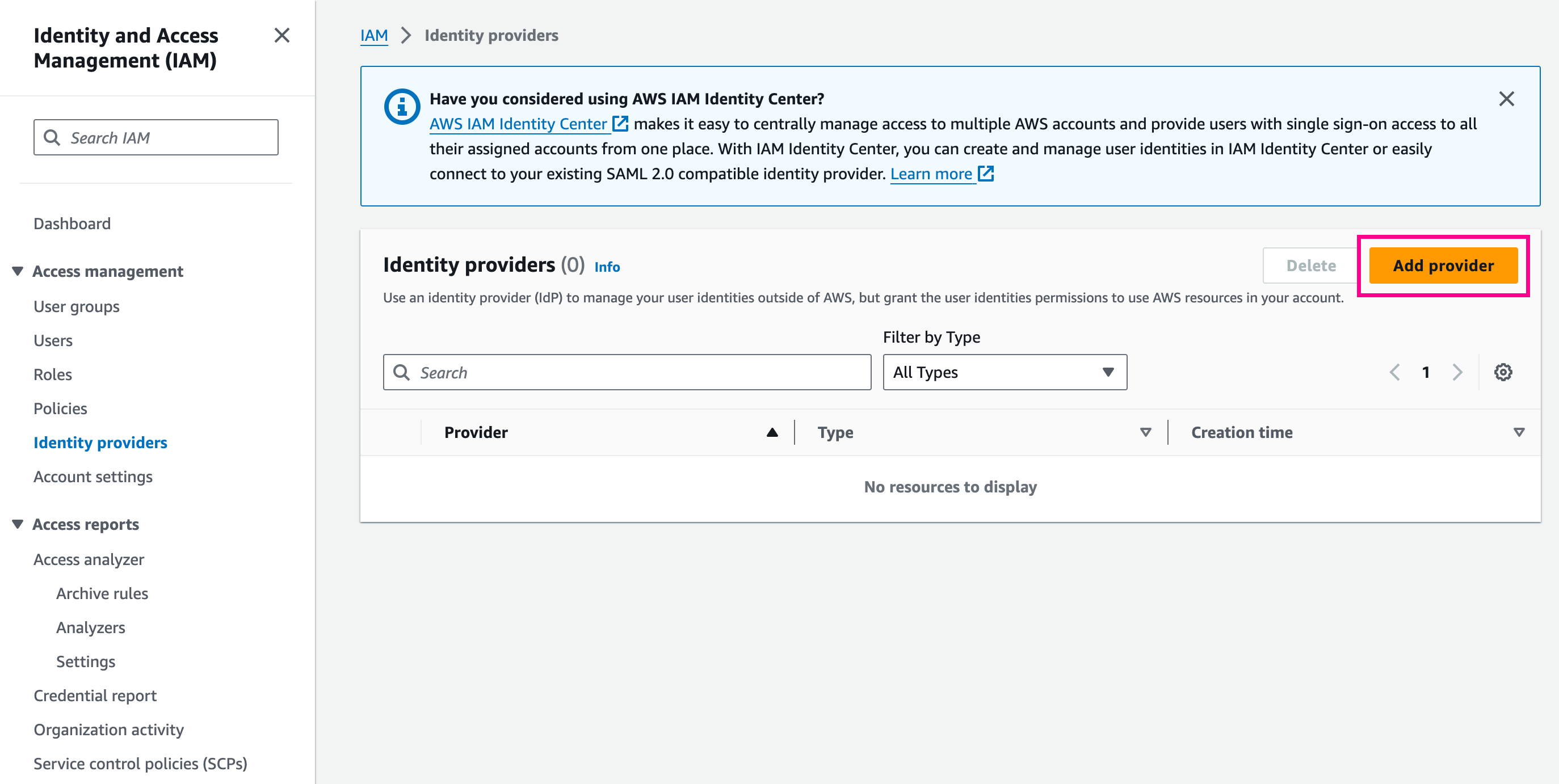
Navigate to your AWS Management Console
-
Go to
-
Select Add Provider
-
Under "Provider Type", select OpenID Connect
-
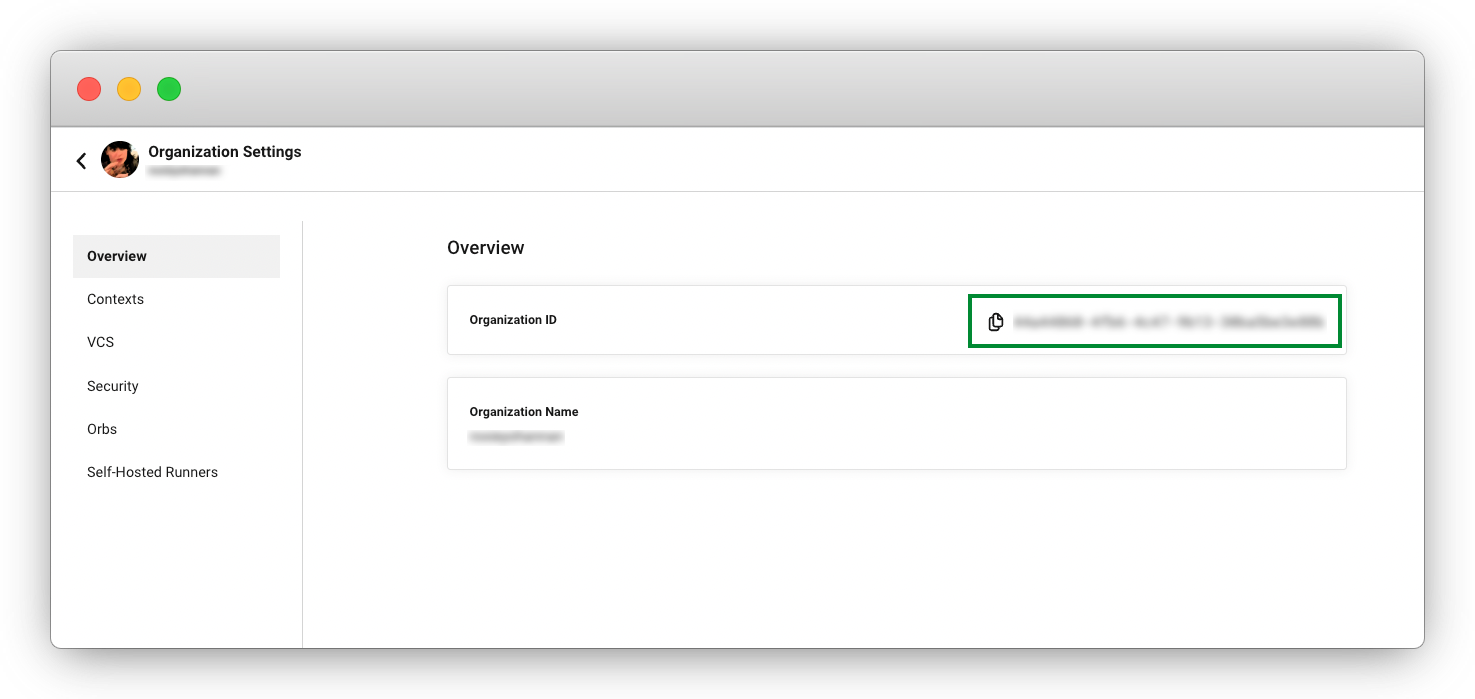
Enter your "Provider URL". This will be
https://oidc.circleci.com/org/<your-organization-id>, where<your-organization-id>is the ID of your CircleCI organization.To find your organization/user ID, select Organization Settings in the CircleCI web app side bar.
-
Select Get Thumbprint.
-
For "Audience" enter your organization ID.
-
Select Add Provider.
b. Policy
-
From your AWS management console, navigate to
-
Select Create Policy.
-
Select JSON to select the JSON policy editor and then copy in the following permissions. We have organized the permissions into two groups. OrbPermissions and S3Access statements are used for the deployment of the model to the endpoints. The S3AccessTrainModel and SageMakerTrainModel statements are needed if you want to train the demo model we provide.
Update the S3 bucket information to match your setup. Create a bucket if one does not yet exist. { "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "OrbPermissions", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "sagemaker:AddTags", "sagemaker:CreateEndpointConfig", "sagemaker:CreateModel", "sagemaker:DescribeEndpoint", "sagemaker:DescribeEndpointConfig", "sagemaker:ListEndpoints", "sagemaker:ListModelPackages", "sagemaker:ListTags", "sagemaker:UpdateEndpoint", "iam:PassRole" ], "Resource": "*" }, { "Sid": "S3Access", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3:GetObject", "s3:ListBucket" ], "Resource": [ "arn:aws:s3:::<BUCKET_FOR_MODEL_ASSETS>/*" ] }, { "Sid": "S3AccessTrainModel", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3:GetObject", "s3:ListBucket", "s3:PutObject" ], "Resource": [ "arn:aws:s3:::sagemaker-sample-files/*", "arn:aws:s3:::circleci-sagemaker-pipeline", "arn:aws:s3:::circleci-sagemaker-pipeline/*" ] }, { "Sid": "SageMakerTrainModel", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "sagemaker:CreateTrainingJob", "sagemaker:DescribeTrainingJob", "logs:DescribeLogStreams", "sagemaker:ListModelPackageGroups", "sagemaker:CreateModelPackage", "sagemaker:UpdateModelPackage" ], "Resource": "*" } ] } -
Scroll down and click Next
-
Give your policy a name and then click Create Policy
c. Role
-
From your AWS management console, navigate to
-
Select Create Role.
-
Select Web Identity and then select the CircleCI provider you created above, and under Audience, select your org ID
-
Use the search function to find the policy you created above by name, select it and click Next
-
Give your Role a name, and then scroll to the Trust policy section. Set up the Trust relationship between the Role and the CircleCI OIDC Provider. Here is an example Policy. Remember to replace the placeholders
<CIRCLECI-ORG-ID>and<CIRCLECI-PROJECT-ID>with your values.{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "Federated": "arn:aws:iam::<AWS-ACCOUNT-ID>:oidc-provider/oidc.circleci.com/org/<CIRCLECI-ORG-ID>" }, "Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity", "Condition": { "StringLike": { "oidc.circleci.com/org/<CIRCLECI-ORG-ID>:sub": "org/<CIRCLECI-ORG-ID>/project/<CIRCLECI-PROJECT-ID>/user/*" } } }, { "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "Service": "sagemaker.amazonaws.com" }, "Action": "sts:AssumeRole" } ] } -
Select Create Role.
-
Select your role from the list and copy the Role ARN, you will need this in the next section.
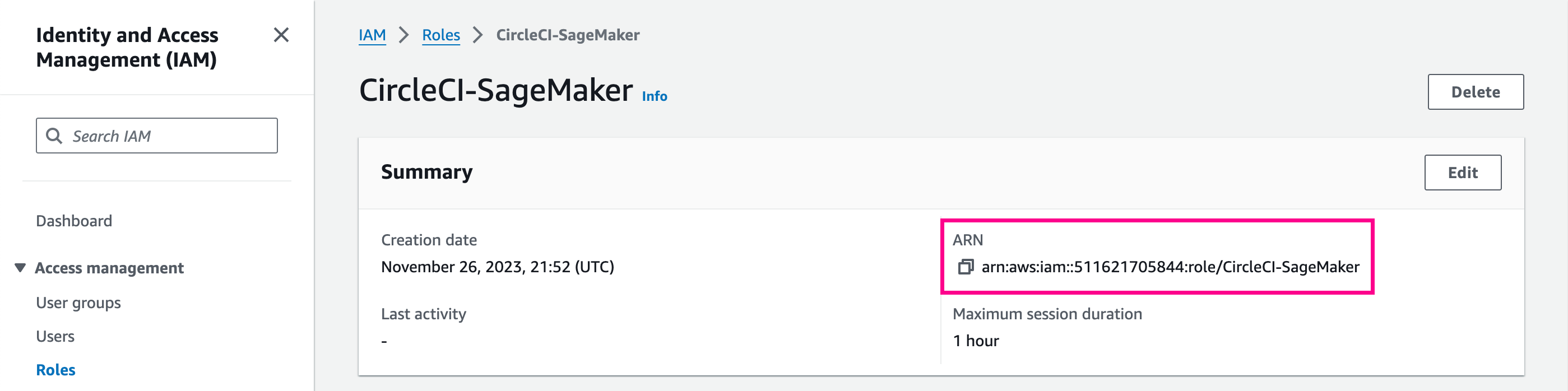
3. Set environment variables
The CircleCI Amazon SageMaker orb requires some environment variables to function. You can store these environment variables at the project level, or you can store them using a context. The following steps show how to add the environment variables at the project level. You need to add two environment variables, as follows:
-
CCI_RELEASE_INTEGRATION_TOKEN: The orb connects your deployment to SageMaker with CircleCI deploys. This gives you visibility into the Endpoint Configuration Updates, and what is currently active. -
SAGEMAKER_EXECUTION_ROLE_ARN: This is the AWS IAM Role you configured with the necessary SageMaker permissions, and the OIDC Trust relationship.
Follow these steps to add the environment variables:
-
In the CircleCI web app, select your org from the org cards on your user homepage.
-
Select Projects from the sidebar and locate your project from the list. You can use the search to help.
-
Select the ellipsis () next to your project and select Project Settings.
-
In the sidebar menu, select Environment Variables.
-
Select Add Environment Variable button to enter a name and value of the new environment variable.
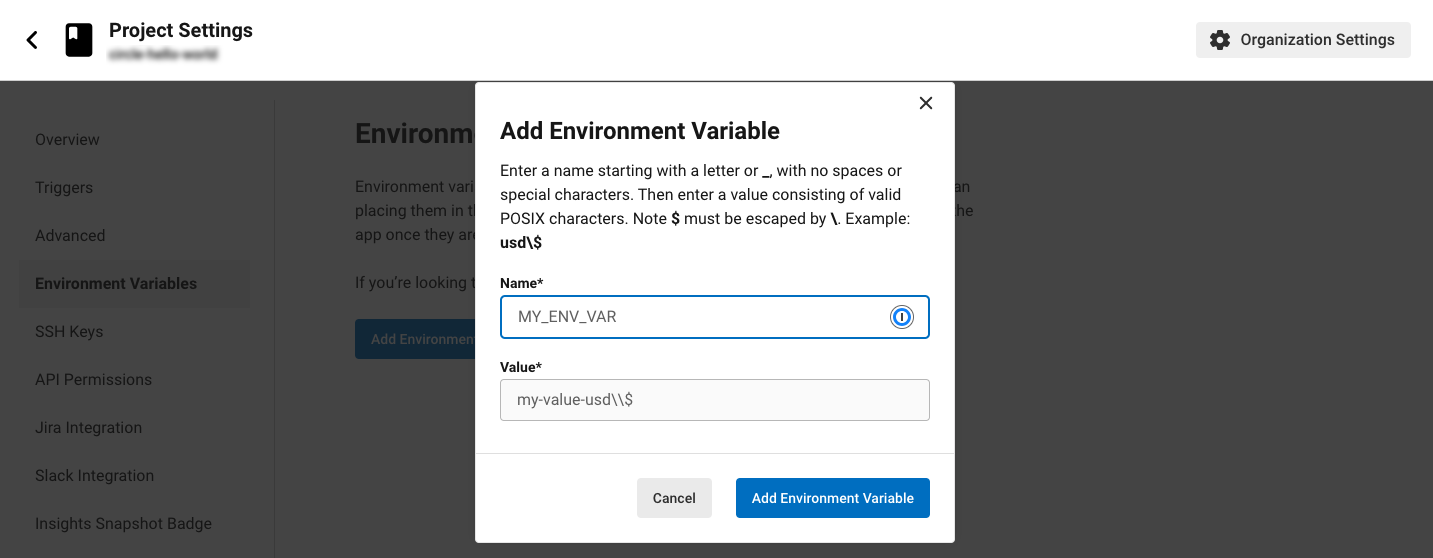
-
Repeat step four for the second environment variable
4. Set up your CircleCI configuration
Take a look at the .circleci/config.yml for the sample project. In the block of pipeline parameters at the top, you need to update the defaults with your values.
parameters:
bucket:
type: string
default: circleci-sagemaker-pipeline
model_desc:
type: string
default: "Kitten Classifier allowing us to distinguish between giraffes and kittens."
model_name:
type: string
default: kitten-classifier
project_id:
type: string
default: "e47ee9b0-446f-44cf-bec8-5407ceb06930"
region_name:
type: string
default: us-east-1Make the following updates:
| Parameter | Default |
|---|---|
| The bucket you set up in the Role Policy |
| A description of your model |
| The name of the model |
| The CircleCI project ID, you can find this on the Project Settings page in the CircleCI web app |
| The region, for example, |
5. Build a model package version
The sample app used in this how-to guide uses a model commonly found in AWS documentation, Abalone. It has just been renamed. If you already have your own model, feel free to adapt the configuration file to use that one instead. All you will need to do is update the model_name parameter.
Assuming you are using our example repository, follow these steps to build a new model package version:
-
A workflow (
model-train) is configured to run on the branchmodel-train. Checkout themodel-trainbranch, and push it up to GitHub -
The
model-trainworkflow will make a new model package version in the model registry. If the model package doesn’t already exist, it will create it.
Every time you run this workflow by pushing to the model-train branch, anew model version is created.
6. Use the orb
Let’s break down the deploy-model-through-to-prod workflow. Our first job is aws-sagemaker/create_model. This job creates a model from your latest Model Package in the registry. This will be what we then deploy to the inference endpoints. In general, create-model just needs to be called one time at the beginning of your workflow:
- aws-sagemaker/create_model:
# job name that will show in Workflow DAG
name: create-model
# s3 bucket where asset will be stored
bucket: << pipeline.parameters.bucket >>
# Name of the model in SageMaker that we will be deploying.
model_name: << pipeline.parameters.model_name >>
# We use the pipeline.id as the unique identifier for some of the configs we create
circle_pipeline_id: << pipeline.id >>
# Region where we are deploying to
region_name: << pipeline.parameters.region_name >>
filters: *main-branch-only-
Aside from
nameandfilters, all other parameters are passed in from our pipeline parameters. -
namecontrols the name of this job visible in the Workflow graph in the CircleCI web app. -
filtersallows you to control what branch the job runs on.
Next, we need to create the endpoint configuration, this happens in the job aws-sagemaker/create_endpoint_configuration:
- aws-sagemaker/create_endpoint_configuration:
name: dev:create-model-endpoint-config
bucket: << pipeline.parameters.bucket >>
model_name: << pipeline.parameters.model_name >>
circle_pipeline_id: << pipeline.id >>
circle_project_id: << pipeline.parameters.project_id >>
region_name: << pipeline.parameters.region_name >>
requires:
- create-model
filters: *main-branch-only-
deploy_environmentis an arbitrary string you can use to bucket your model releases, for example,dev,staging,testing,prod. In our example config, you can see we are only using two,devandprod.
Next, we need to push out the updated configuration, this happens in the job aws-sagemaker/deploy_endpoint:
- aws-sagemaker/deploy_endpoint:
name: dev:deploy-model-to-endpoint
bucket: << pipeline.parameters.bucket >>
model_name: << pipeline.parameters.model_name >>
# Description for the model. q: can we make it optional?
circle_pipeline_id: << pipeline.id >>
circle_project_id: << pipeline.parameters.project_id >>
model_desc: << pipeline.parameters.model_desc >>
# You can find this value in the Project Settings in CircleCI
region_name: << pipeline.parameters.region_name >>
requires:
- dev:create-model-endpoint-config
filters: *main-branch-only-
The only thing to set here is the
deploy_environmentso we know whatendpoint_configurationto use. This will deploy your endpoint configuration.
Next, is an approval job. This stops the workflow from deploying to production until a human approves it. When this does get approval, we then repeat the above steps of aws-sagemaker/create_endpoint_configuration and aws-sagemaker/deploy_endpoint but with deploy_environment set to prod.:
- promote-model-to-prod-endpoint:
type: approval
requires:
- dev:deploy-model-to-endpoint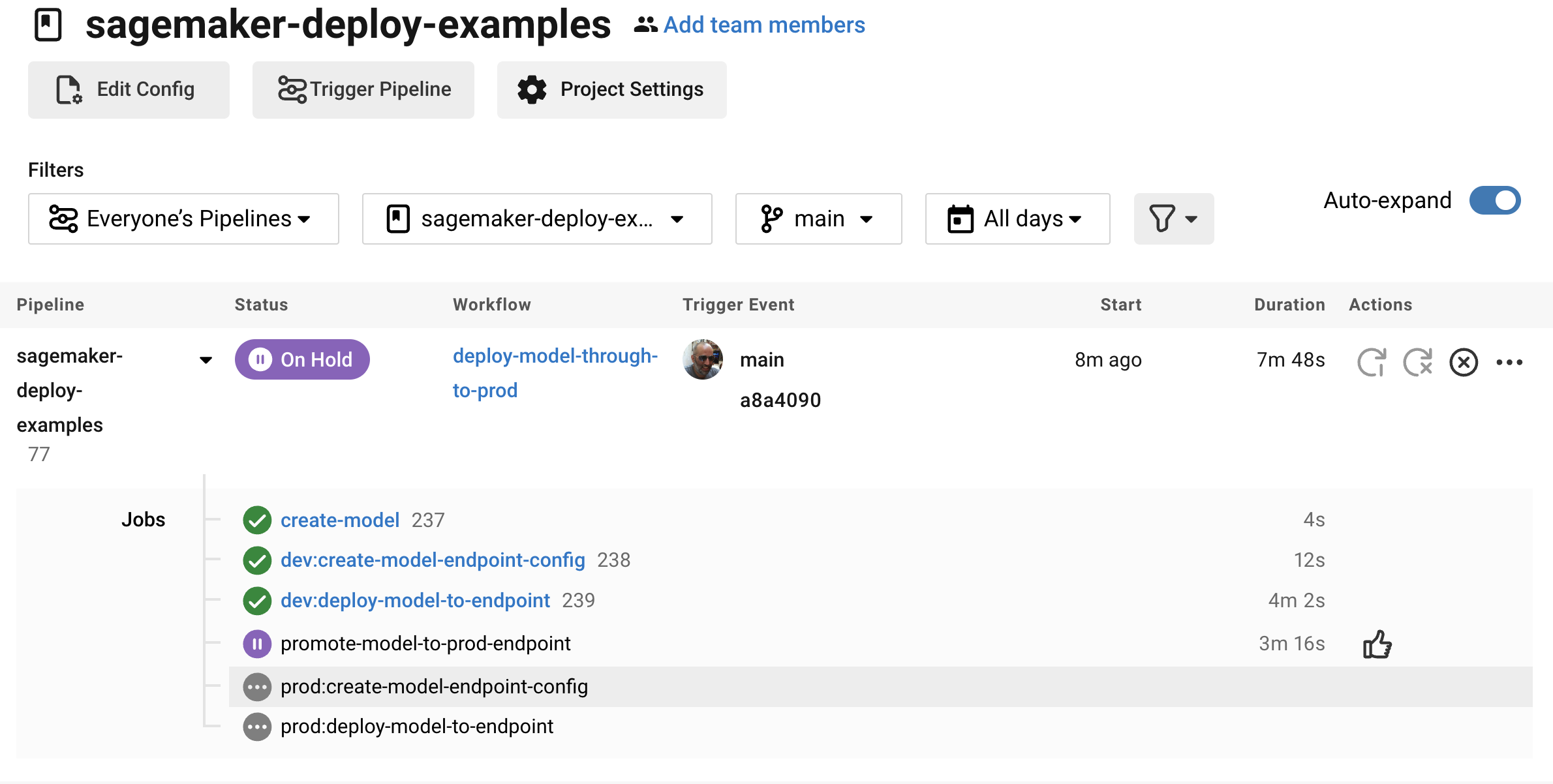
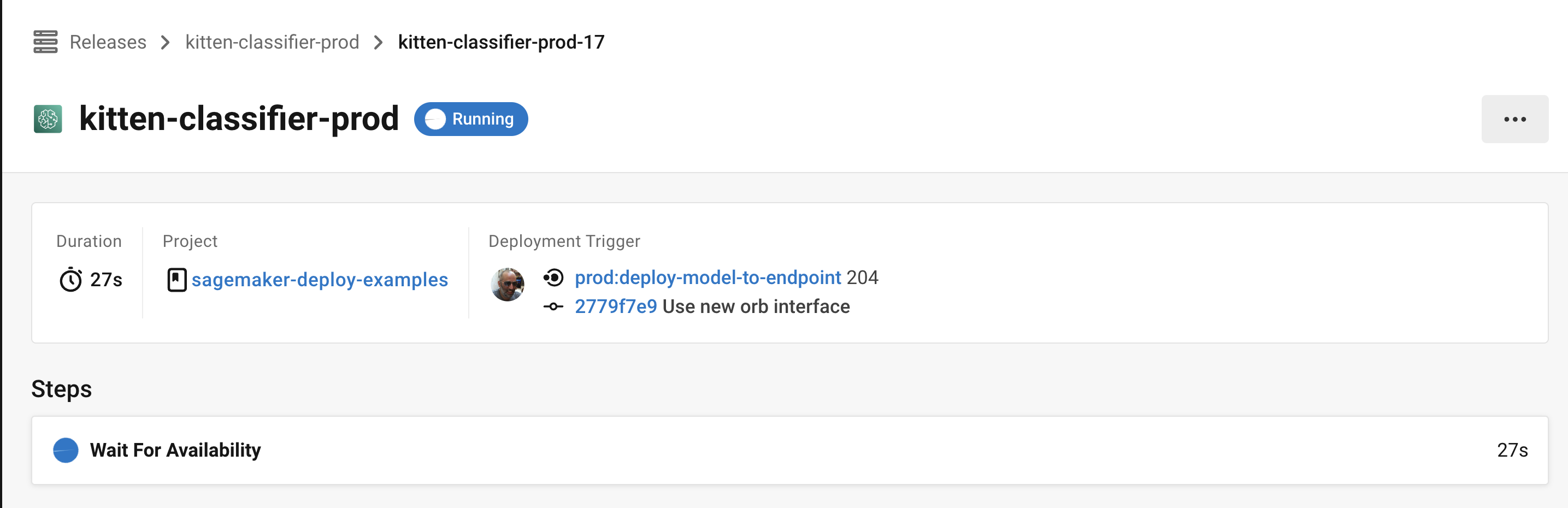
7. Check in on your deployment
The CircleCI deploys UI offers you a single pane of glass to monitor all your deployments across environments. You can view deployment progress in real time, see what versions are currently deployed, and navigate to the SageMaker console. If you navigate to the deploys dashboard by clicking Deploys in the web app sidebar, you should now see something along the lines of the image below:
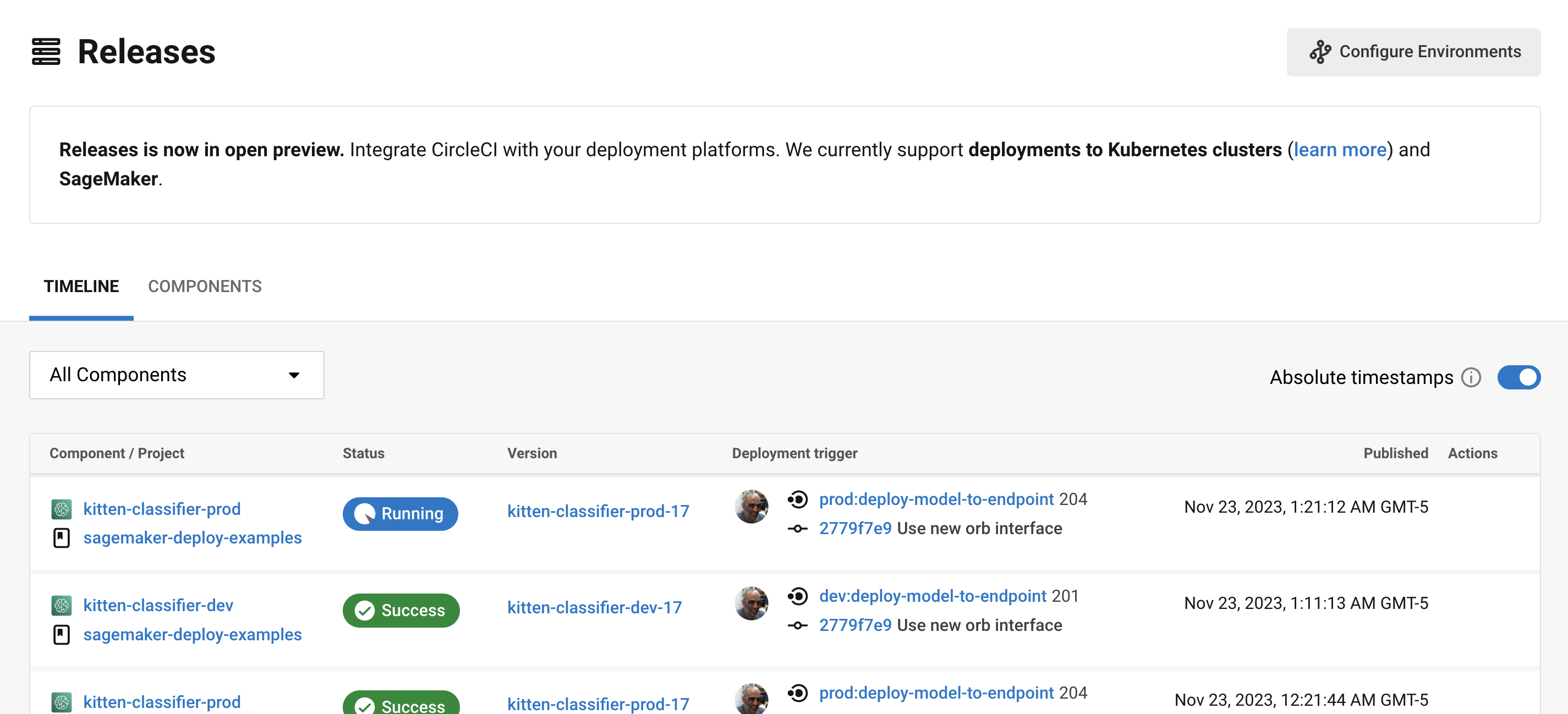
Select the component name to view details about the component, including the number of instances deployed. From this interface, you can navigate to Amazon SageMaker for live information on your endpoint.
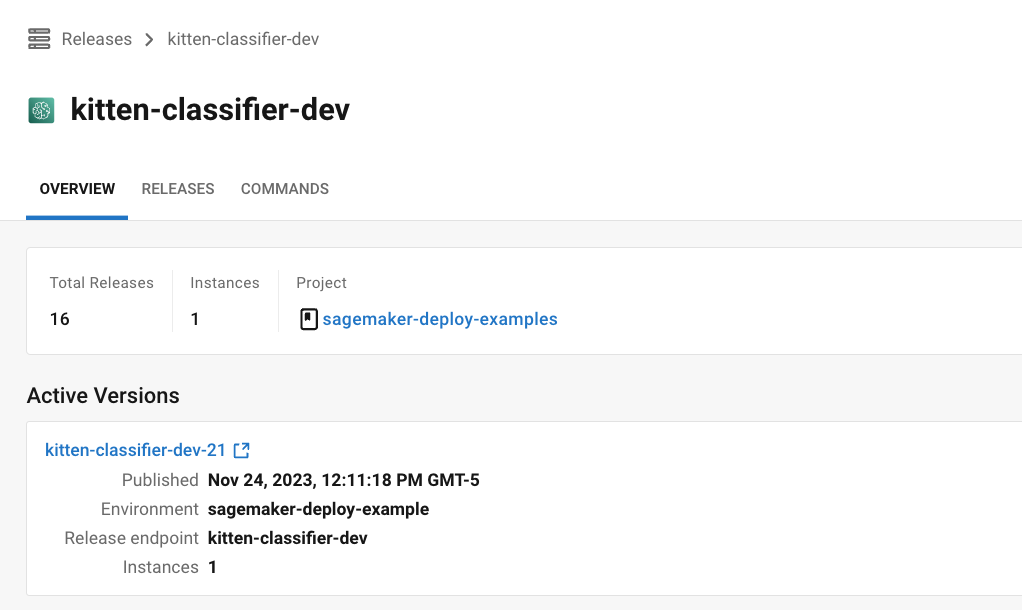
Select the version to see the details page for the version being deployed. Clicking on a specific version lets you monitor deployment progress in real-time.