Audit logs
Overview
CircleCI logs important events in the system for audit and forensic analysis purposes. Audit logs are separate from system logs that track performance and network metrics.
If you have administrator permissions for your organization, you can access the audit log feature from the UI in the web app:
-
Select Organization Settings in the web app sidebar.
-
Select Security from the menu.
-
Scroll down to the Audit Log section and specify a date range.
-
Click Request audit logs to download audit logs as a CSV file. Audit log fields with nested data contain JSON blobs.
In some situations, the internal machinery may generate duplicate events in the audit logs. The id field of the downloaded logs is unique per event and can be used to identify duplicate entries. |
Per our data retention policy, audit logs can be retrieved for up to 12 months.
Audit log events
The following list shows common and important events found in the audit log. This list is not comprehensive, and you may see additional action types logged that are not represented below. See action in the Field section below for the definition and format.
-
checkout-key.create
-
checkout-key.delete
-
checkout-key.delete-all
-
context.create
-
context.delete
-
context.secrets.accessed
-
context.env_var.delete
-
context.env_var.store
-
deploy-keys.delete
-
project.env_var.create
-
project.env_var.delete
-
project.settings.update
-
project.ssh_key.create
-
project.ssh_key.delete
-
project.api_token.create
-
schedule.create
-
schedule.update
-
schedule.delete
-
workflow.job.approve
-
workflow.job.finish
-
workflow.job.scheduled
-
workflow.job.start
-
org.workflows.deleted
Audit log fields
-
action: The action taken that created the event. The format is ASCII lowercase words, separated by dots, with the entity acted upon first and the action taken last. In some cases entities are nested, for example,workflow.job.start. -
actor: The actor who performed this event. In most cases this will be a CircleCI user. This data is a JSON blob that will always containidandtypeand will likely containname. -
target: The entity instance acted upon for this event, for example, a project, an org, an account, or a build. This data is a JSON blob that will always containidandtypeand will likely containname. -
payload: A JSON blob of action-specific information. The schema of the payload is expected to be consistent for all events with the sameactionandversion. -
occurred_at: When the event occurred in UTC expressed in ISO-8601 format with up to nine digits of fractional precision, for example '2017-12-21T13:50:54.474Z'. -
metadata: A set of key/value pairs that can be attached to any event. All keys and values are strings. This can be used to add additional information to certain types of events. -
id: A UUID that uniquely identifies this event. This is intended to allow consumers of events to identify duplicate deliveries. -
version: Version of the event schema. Currently the value will always be 1. Later versions may have different values to accommodate schema changes. -
scope: If the target is owned by an Account in the CircleCI domain model, the account field should be filled in with the Account name and ID. This data is a JSON blob that will always containidandtypeand will likely containname. -
success: A flag to indicate if the action was successful. -
request: If this event was triggered by an external request, this data will be populated and may be used to connect events that originate from the same external request. The format is a JSON blob containingid(the unique ID assigned to this request by CircleCI).
Request audit logs from the web app
All CircleCI customers can request audit logs from the web app. To have access to this feature, cloud customers must be organization admins.
Frequency limits for requests are as follows:
-
Free Plan: 1 request per day
-
All paid plans: 3 requests per day
-
Maximum query window for 30 days - specifically, a customer can request logs for any 30 day window where the start of the window is within the last calendar year
If your organization has reached the maximum amount of requests per 30 days, the audit log request feature will be disabled. If you hover over the disabled Request audit logs button, a tooltip will appear displaying the date when new requests can be made. Pending requests count toward the rate limit.
| CircleCI may update the quantity and request period in the future. |
Navigate to Organization Settings > Security to view the Audit Log section. Select a date range from the dropdown, then click the Request audit logs button. The earliest start date is one year ago from the current day, and the latest end date is the current day. The data available will depend on the data retention period set per organization, so the returned time period for the data could be less than the requested timeframe.
| Submitted dates are in UTC. To avoid issues arising from potential time zone differences, CircleCI adds extra time to the request. For example, if you request August 2 - August 5, the returned results will be in the range August 1 - August 6. The audit log request column is also displayed in UTC. |
Audit log status
In the UI, a status request will show the following information:
-
Timeframe requested
-
User who made the request
-
Date request was made
-
Expiry date of the request
-
Request status (success, failed, requested)
Successful requests can be active with a download link, active without any data (no download link), or expired (no longer available to download). Successful requests can be downloaded for 30 days.
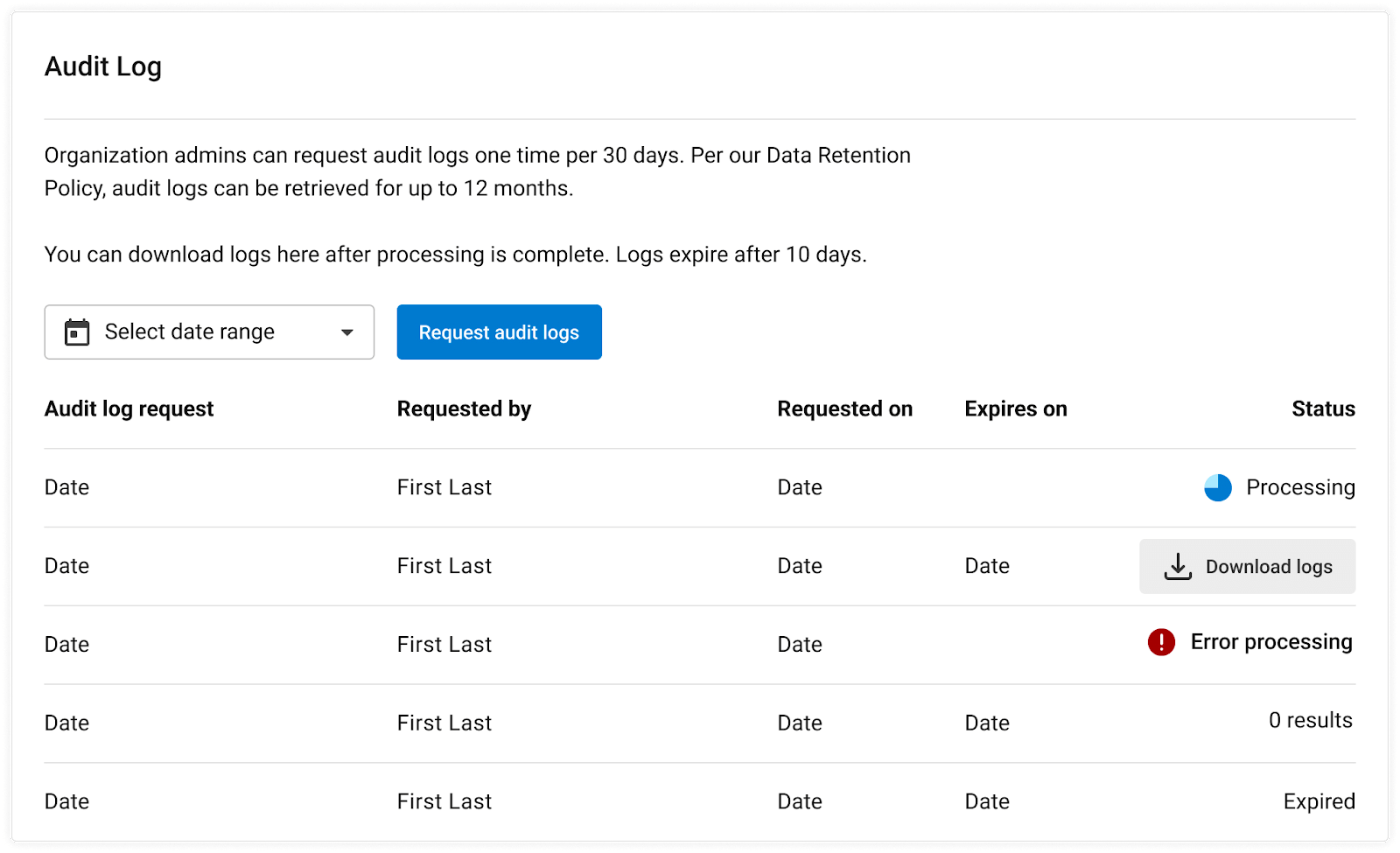
Statuses are updated once per hour on the 30-minute mark (for example, 09:30, 10:30, 11:30).