Machine runner installation on Windows
On This Page
- Prerequisites
- Self-hosted runner terms agreement
- 1. Create namespace and resource class
- 2. Set launch agent version (server only)
- 3. Machine runner installation on Windows
- Machine runner configuration example
- Uninstall / reinstall steps
- Continuous mode vs. single task mode for Windows self-hosted runners
- Troubleshooting
| This installation method is deprecated for CircleCI cloud customers. Refer to the machine runner 3.0 installation guide for the recommended steps to set up Windows self-hosted runners on CircleCI cloud. |
This page describes how to install machine runner on Windows for CircleCI server. This has been tested for Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server 2016, both in Datacenter Edition. Other Server SKUs with Desktop Experience and Remote Desktop Services should also work.
The page below walks you through installing a machine runner and its dependencies (for example, Chocolatey, Git, and Gzip) on your Windows Server.
Since this setup creates a new local administrator user that runs CircleCI jobs, your Windows Server needs to be capable of creating local users and accepting remote logons for them.
The Windows Server needs to be a domain member when you set this up in domain environments. The self-hosted runner instance cannot run on a Windows Server operating as a domain controller.
Prerequisites
-
The CircleCI CLI if you wish to install runners from the command line
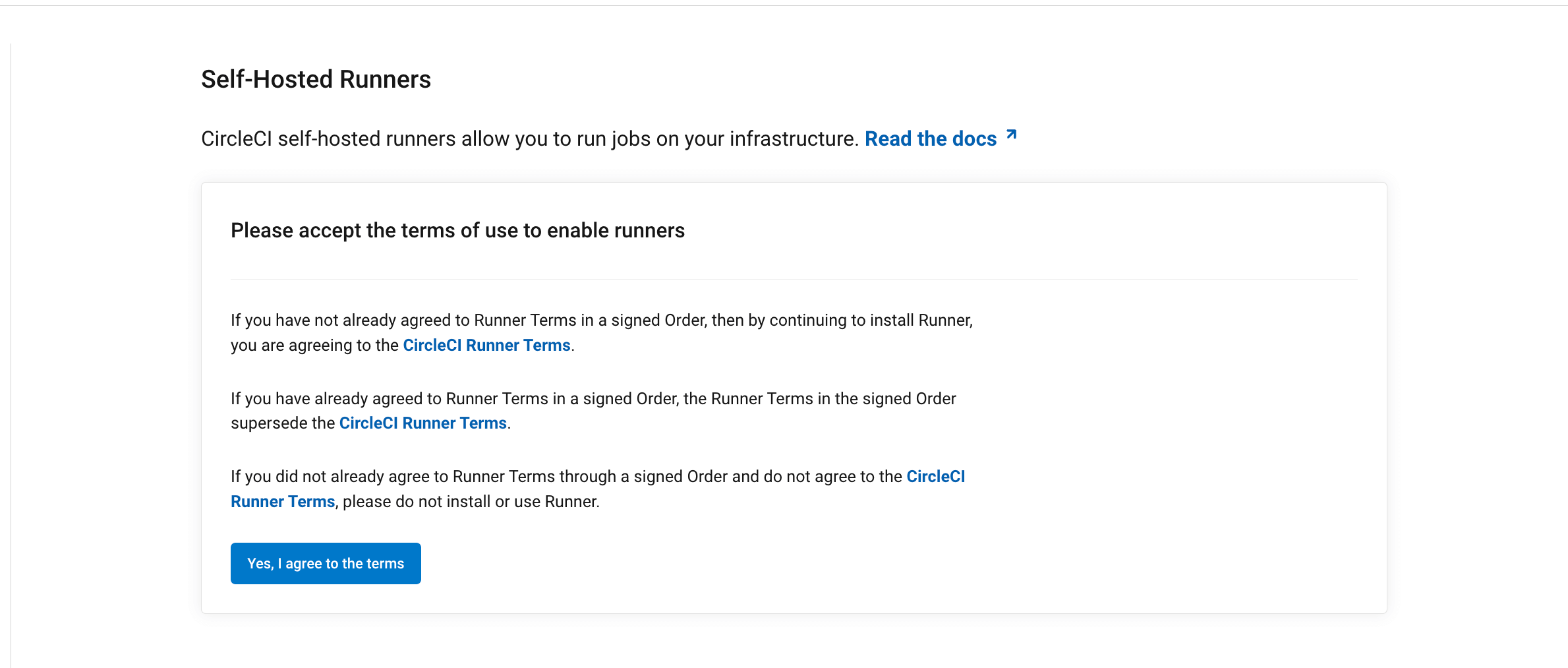
Self-hosted runner terms agreement
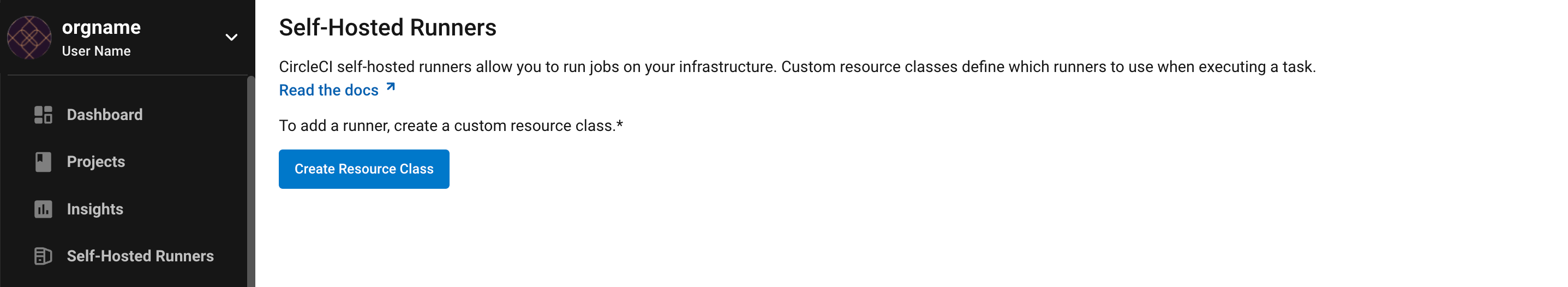
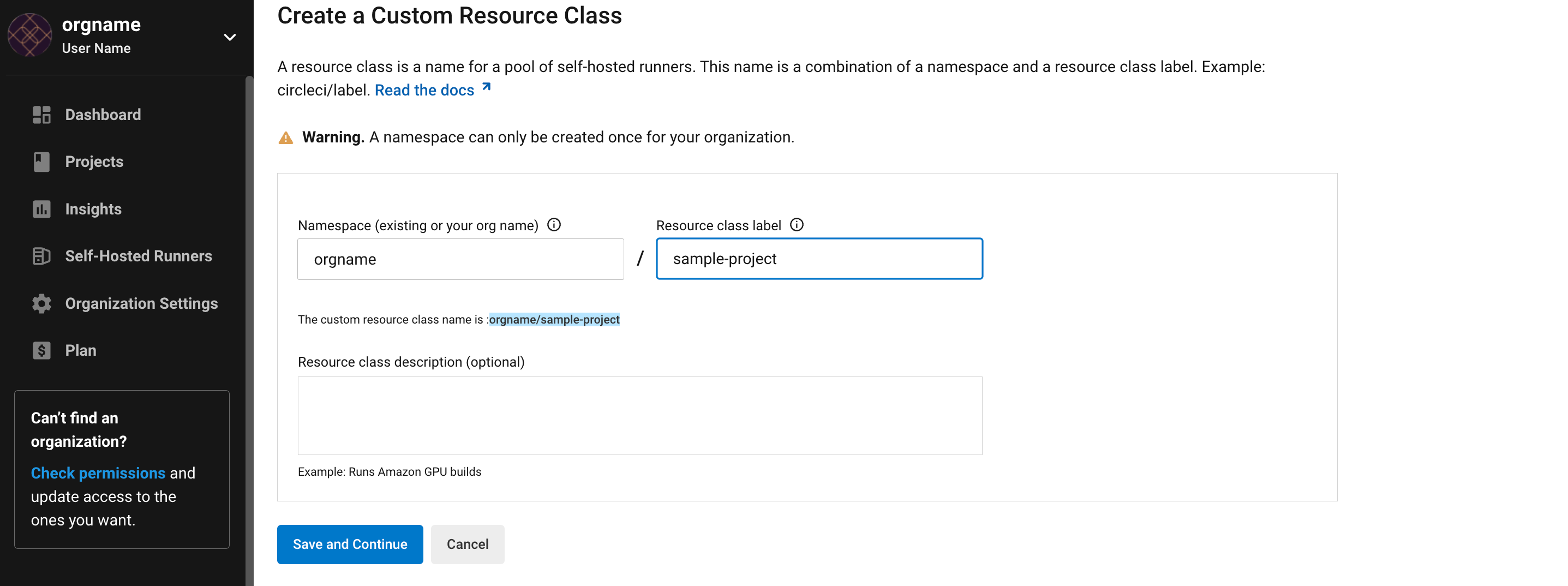
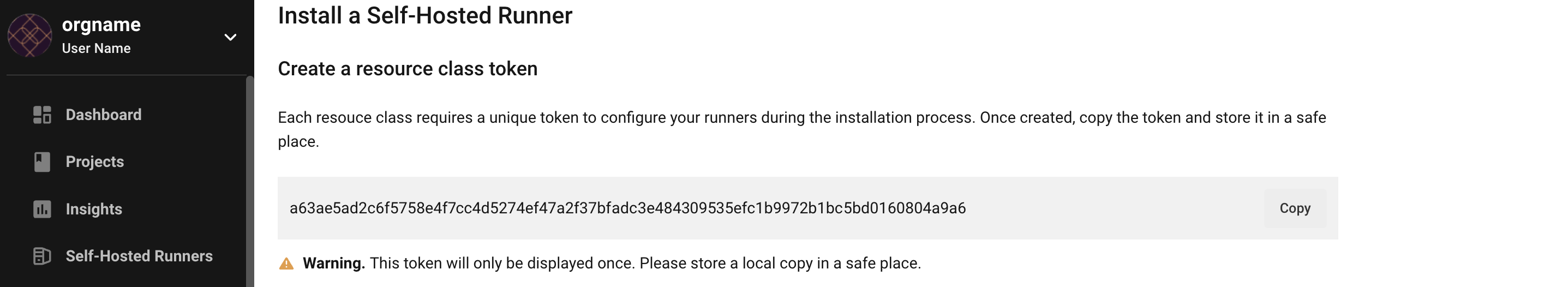
1. Create namespace and resource class
2. Set launch agent version (server only)
-
For server v3.1.0 and up, use the table below to find the compatible machine runner launch-agent version for the version of server you are running:
Server version Launch agent version 3.0
Runner not supported
3.1
1.0.11147-881b608
3.2
1.0.19813-e9e1cd9
3.3
1.0.29477-605777e
3.4
1.1.73695-40bf772
4.0
1.1.73695-40bf772
4.1
1.1.73695-40bf772
4.2
1.1.73695-40bf772
4.3
1.1.73189-8792751
Substitute
<launch-agent-version>with your launch-agent version for server and run the following:$Env:agentVer = "<launch-agent-version>"
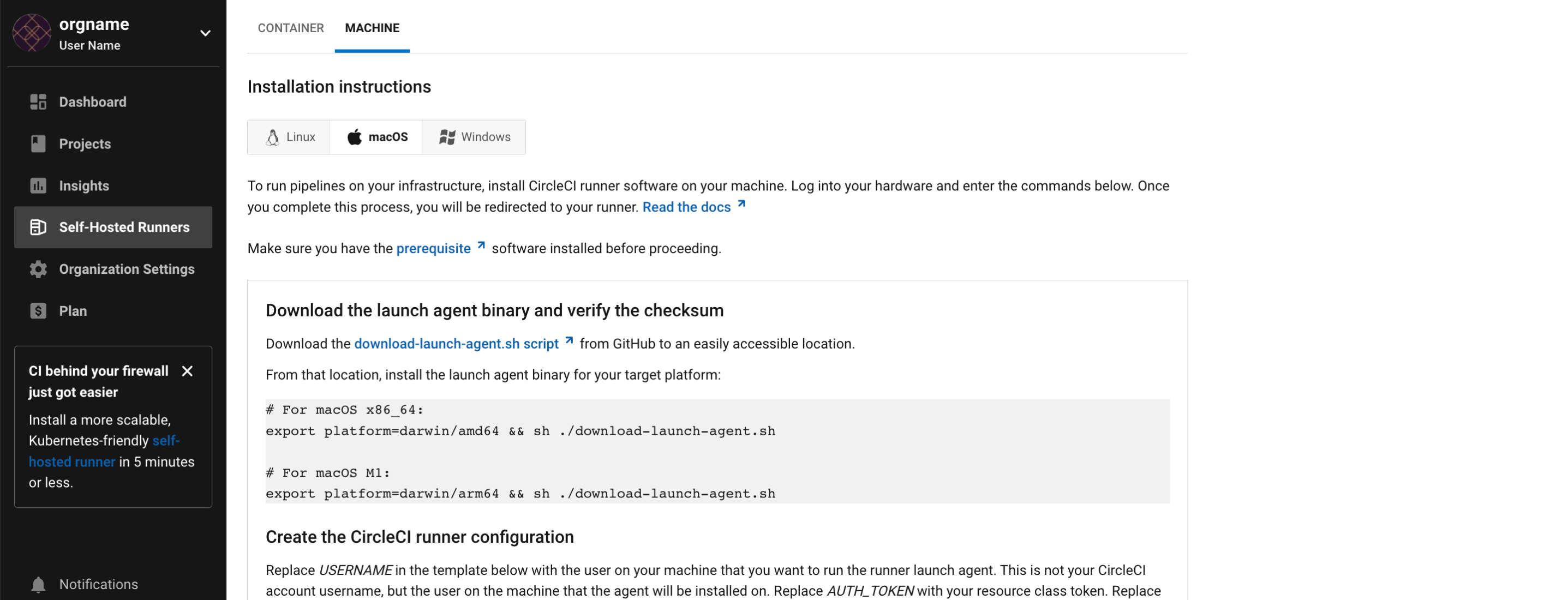
3. Machine runner installation on Windows
-
Download the
Install-CircleCIRunner.ps1script from GitHub to an easily accessible location. -
Open PowerShell as an administrator and navigate to the directory where you placed the script file.
-
Run the following in your PowerShell:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol -bor 3072; ./Install-CircleCIRunner.ps1The installation will be output into your PowerShell interface.
-
As part of the installation, the configuration file for the machine runner (
launch-agent-config.yaml) will open in Notepad. Fill the file out with the requested information (see Self-hosted Runner Configuration Reference). The configuration file is located in the installation directory,C:\Program Files\CircleCI, by default.
After setup completes, the machine runner starts automatically and begins looking for jobs to process.
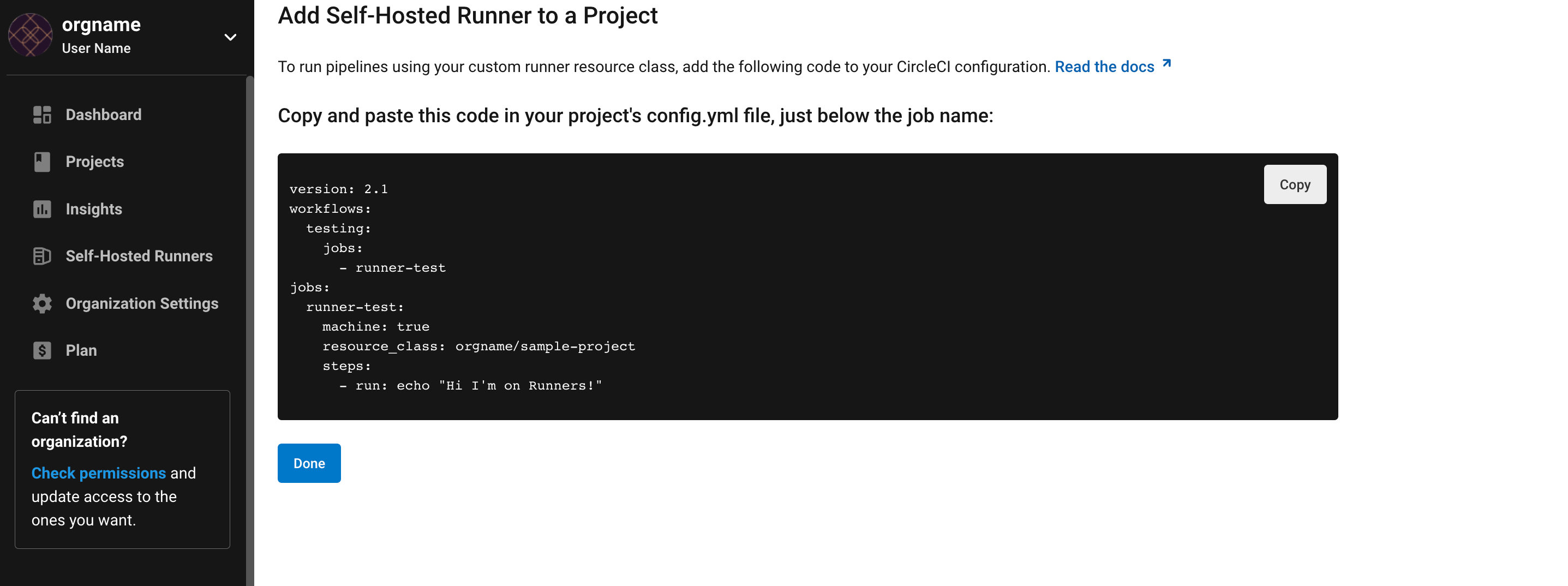
Machine runner configuration example
The fields you must set for a specific job to run using your machine runners are:
-
machine: true -
resource_class: <namespace>/<resource-class>
Simple example of how you could set up a job:
version: 2.1
workflows:
build-workflow:
jobs:
- runner
jobs:
runner:
machine: true
resource_class: <namespace>/<resource-class>
steps:
- run: echo "Hi I'm on Runners!"Uninstall / reinstall steps
Uninstalling machine runners will prepare the system for installation again.
-
Download the
Uninstall-CircleCIRunner.ps1script from GitHub to an easily accessible location. -
Open PowerShell as an administrator and navigate to the directory where you placed the script file.
-
Run the following in your PowerShell:
./Uninstall-CircleCIRunner.ps1
Continuous mode vs. single task mode for Windows self-hosted runners
By default, Windows machine runners run in single task mode in order to ensure high reliability of the underlying technology that the self-hosted runner uses to execute jobs. This is the recommended mode for Windows machine runners.
A Windows machine runner can be run in continuous mode, however, doing so eliminates the guarantee of a clean job environment. This may translate into jobs not executing as expected and failing.
Troubleshooting
Refer to the Troubleshoot Machine Runner section of the Troubleshoot Self-hosted Runner guide if you encounter issues installing or running machine runner on Windows.