GitLab CI/CD integration overview
On This Page
- What is GitLab CI/CD?
- Steps to integrate GitLab projects with CircleCI
- Limitations
- Trigger a pipeline in CircleCI
- Project settings - GitLab
- People
- Pipelines and triggers
- Advanced
- GitLab project SSH keys
- Create GitLab SSH key
- Organization settings - GitLab
- People
- Integrations (GitLab self-managed only)
- Establish the authenticity of an SSH host
- Roles and permissions
- User settings
- Account integrations
- Deprecated system environment variables
- Coming soon
- Account integrations
- Passing secrets to forked pull requests
- Scheduled pipelines
- Stop building
- Additional SSH keys only
- Free and open source setting
- Test Insights
- CircleCI self-hosted server product
- Next steps
- Relevant GitLab articles
This page walks you through integrating a GitLab project with CircleCI. The sections below introduce you to concepts and ways to manage CI/CD (continuous integration and continuous delivery) pipelines for your GitLab project. CircleCI features that are in development for GitLab projects are detailed in the Coming soon section.
What is GitLab CI/CD?
GitLab CI/CD allows you to build, test (continuous integration) and deploy (continuous deployment, continuous delivery) your projects each time a developer pushes a change to the codebase, and/or when a merge request is created. As an alternative, you can integrate with CircleCI to manage your CI/CD pipelines. If you use GitLab (SaaS or Self-managed) for version control and code storage, GitLab CI/CD is enabled for your project by default.
Integrate with CircleCI to access features for automated software delivery:
-
Control over security and permissions, and org-level control with config policies
-
Managed execution environments (Docker, Linux VM, macOS, Windows, Arm VM, GPU), plus self-hosted runners
-
Test integrations, and test-splitting to reduce length of the testing phase of your pipelines
-
Packaged config (orbs) to simplify integration with many third party platforms, services, language tools etc.
-
Developer tools: CircleCI CLI, APIs, and VS Code extension, config SDK
Steps to integrate GitLab projects with CircleCI
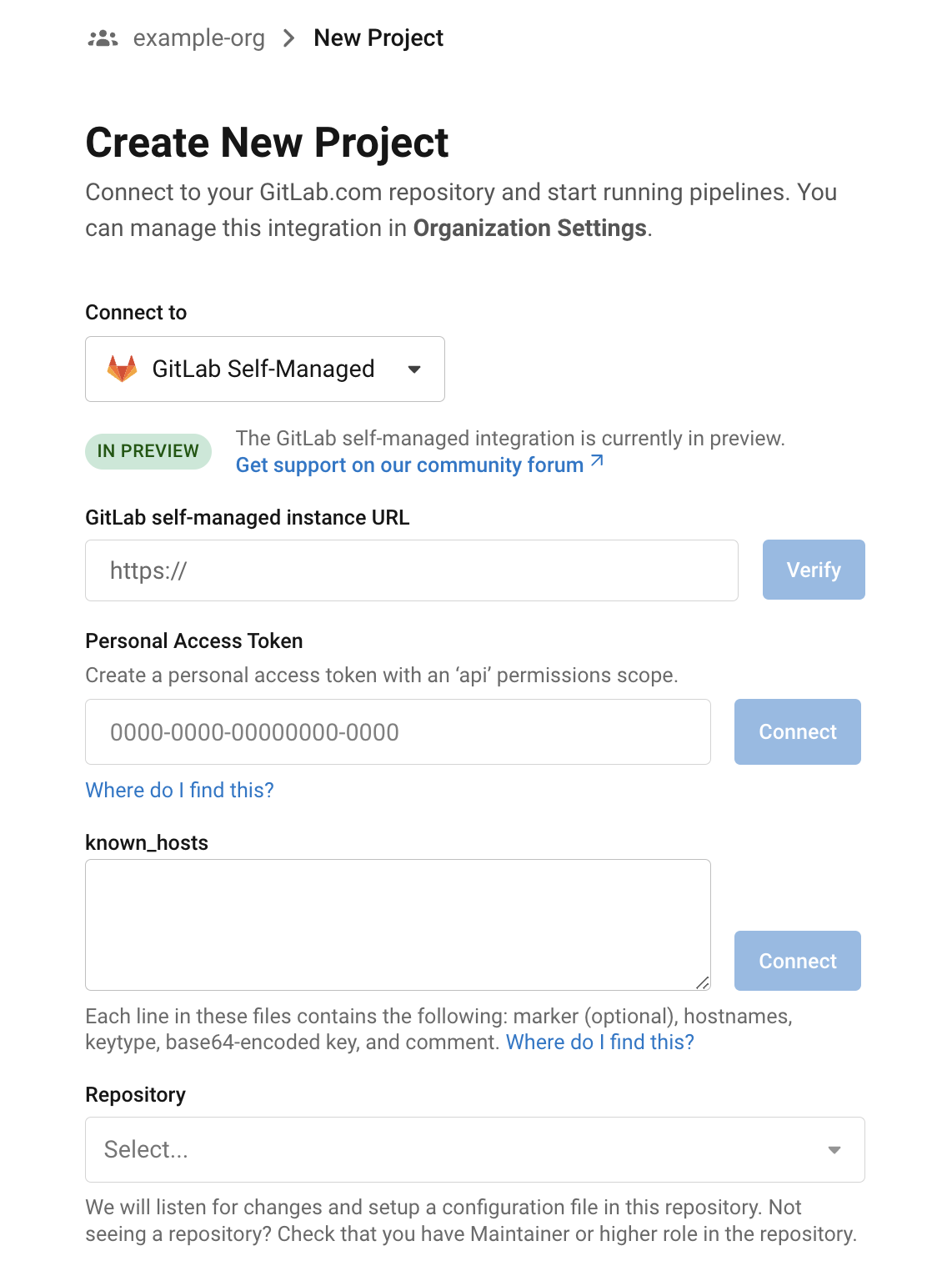
Follow the steps on the Sign up and try CircleCI page to connect your GitLab account, which creates your CircleCI organization.
| You will need API access and write permissions on the repository you want to set up. Within GitLab, this is the "maintainer" role or higher. |
Remove GitLab CI/CD config You should remove the .gitlab-ci.yml file from projects you integrate with CircleCI. This prevents you from having CI/CD builds happening in both systems. There is an option to disable GitLab CI/CD for a project in the GitLab UI but using this is not recommended. |
When you create a new organization and connect your GitLab.com account, you will be prompted to create a new project from a repository. You may select a repository in which you have already created a .circleci directory at the root of the repository, with a config.yml file in that directory.
If your selected repository does not already have a .circleci/config.yml, you will be presented with the following options to set up a CircleCI configuration for your project:
-
Fastest: Use an existing
config.ymlin one of your repositories.You can select another repository in your account that has previously been set up with a CircleCI configuration. The
.circleci/config.ymlfile may be in the main branch, or a feature branch. The config is imported into your new project—CircleCI automatically creates a new branch and adds a commit for you. -
Faster: Commit a starter CI pipeline to a new branch.
CircleCI automatically creates a new branch and commits a basic configuration file. You may make further changes to the file afterwards in your GitLab repository.
-
Fast: Use a
config.ymltemplate that you can edit and save.You can choose a sample
.circleci/config.ymlto best fit your project from a variety of templates (for example, Node.js, Python, iOS apps). You can make changes to the file in CircleCI before saving. The config is committed on a new branch.
The first two options (Fastest and Faster) automatically trigger a pipeline once you create the project.
If you are new to CircleCI, you may wish to get started with our Hello world example, or take a look at some of our sample configurations that demonstrate different types of workflows. The Configuring CircleCI page is a full reference to the keys used in a .circleci/config.yml file. |
When you connect a repository with your CircleCI project, behind the scenes, CircleCI is registering a webhook within your GitLab repository. You may verify this once you have successfully created the project by navigating to your repository’s Settings > Webhooks page.
Limitations
The following limits are currently in place for GitLab integrations:
-
Each user can create up to three organizations.
-
Each organization under a Free Plan can have up to 10 projects.
If you need more organizations or projects, consider upgrading to a Paid plan, or contact our Support team.
Trigger a pipeline in CircleCI
When you create a new project using the Fastest (use an existing config.yml) or Faster (commit a starter CI pipeline) options described in the section above, a pipeline is automatically triggered. You should see the pipeline running shortly after you are taken to the CircleCI dashboard.
If you use the Fast config setup, the pipeline is not triggered until you save the .circleci/config.yml by clicking the Commit and Run button in the web app.
Each time you push changes to your GitLab repository, a new pipeline is triggered and you should see it running for the project within the CircleCI web app.
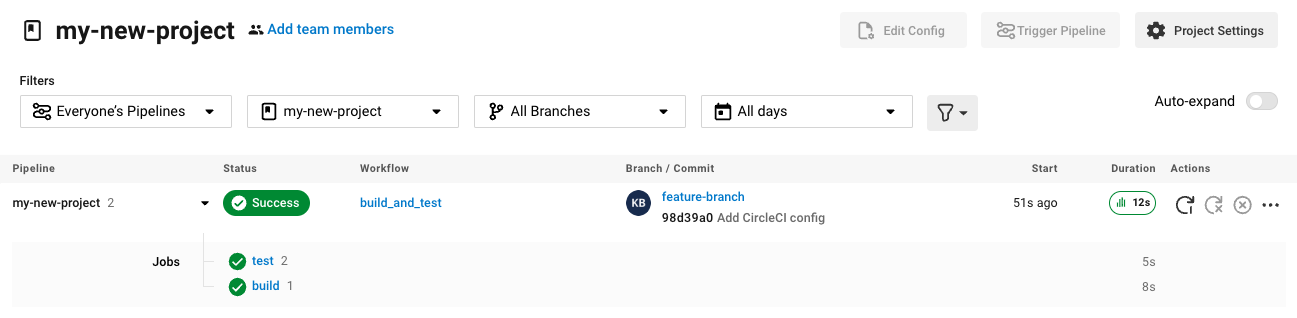
Editing an existing CircleCI configuration within the web app is not currently available. You may make further changes to the config in your GitLab repository.
Committing further changes in your repository will automatically trigger a pipeline. However, manually triggering a pipeline from the CircleCI web app is also not available at this time.
Project settings - GitLab
Within CircleCI, a project integrated from GitLab can have one or more configurations, which are pipeline definitions. Configurations include, but are not limited to, a .circleci/config.yml file in your repository.
A project can have one or more triggers, which are events from a source of change. Triggers include, but are not limited to, a VCS. A trigger determines which configuration should be used to start a pipeline.
The following settings are found by clicking the Project Settings button within your project. At this time, both configurations and triggers are limited to GitLab integrations.
People
Project roles give control over which users have access to which projects within an organization. This enables teams to have limited access to only their projects, while managers and others can have broader organizational access. The access options are:
-
Admin: Read and write access to the project and all settings and ability to manage other users' access.
-
Contributor: Read and write access to the project and some settings.
-
Viewer: Read only access to the project and some settings.
For a complete list of permissions, see the Roles and permissions overview page.
Pipelines and triggers
You can add or delete pipelines and triggers for your project. For details see the pipelines overview.
Advanced
-
You can enable dynamic configuration using setup workflows in CircleCI. To learn about dynamic configuration, read the Dynamic configuration guide.
-
At this time, the Free and Open Source setting is not currently supported for GitLab integrations.
GitLab project SSH keys
When creating a GitLab-based project in CircleCI, an SSH key is created, which is used to check out code from your repository. Each configuration you create generates a new SSH key to access the code in the repository associated with that configuration. At this time, only Additional SSH Keys are applicable to GitLab projects.
Create GitLab SSH key
-
Create an SSH key-pair by following the GitLab instructions. When prompted to enter a passphrase, do not enter one (below is one example command to generate a key on macOS):
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "your_email@example.com" -
Go to your project on GitLab and navigate to Settings > Repository, and expand the Deploy keys section. Enter a title in the "Title" field, then copy and paste the public key you created in step 1. Check Grant write permissions to this key box, then select Add key.
-
Go to your project settings in the CircleCI app, select SSH Keys, and Add SSH key. In the "Hostname" field, enter
gitlab.comand add the private key you created in step 1. Then select Add SSH Key. -
In your
.circleci/config.ymlfile, add the fingerprint to a job using theadd_ssh_keyskey:version: 2.1 jobs: deploy-job: steps: - add_ssh_keys: fingerprints: - "SO:ME:FIN:G:ER:PR:IN:T"
When you push to your GitLab repository from a job, CircleCI will use the SSH key you added.
For more information on SSH keys, refer to the Adding an SSH key to CircleCI page.
Organization settings - GitLab
For GitLab integrations, organizations and users are managed independently from your VCS. Organizations and users are considered CircleCI organizations and users, with their own roles and permissions that do not rely on those defined in your VCS.
To manage settings at the organization level, select Organization Settings in the CircleCI web app sidebar.
People
Add or remove users, and manage user roles for the organization as well as user invites. See the Roles and permissions overview page for full details.
Integrations (GitLab self-managed only)
For GitLab Self-managed organizations, you may connect additional self-managed instances to be integrated with your organization.
-
Navigate to Integrations within Organization Settings to add a new instance.
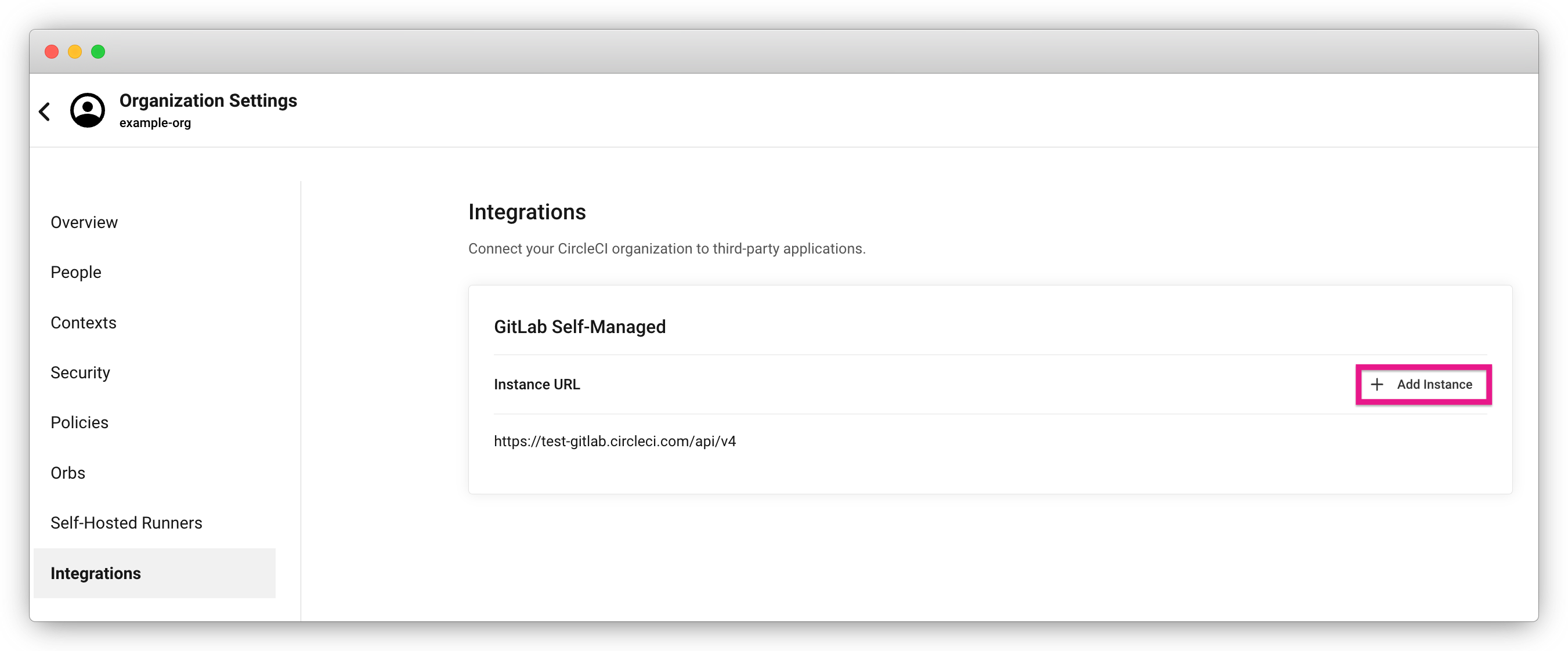
-
You will need to enter the instance URL, as described in the Sign up section above.
| The ability to edit or delete existing integrations is not currently supported. |
For GitLab.com, account integrations can be managed under your user settings.
Establish the authenticity of an SSH host
For GitLab self-managed instances, it is necessary to add the SSH host keys to a "known hosts" file (~/.ssh/known_hosts) so that CircleCI can verify that the host it is connecting to is authentic. The known_hosts input stores your instance’s public host keys so CircleCI jobs can verify the remote host’s identity when checking out code.
SSH keys for remote servers can be fetched by running ssh-keyscan <host>, for example, ssh-keyscan test-gitlab.circleci.com.
When retrieving the host keys, you can confirm that you have the correct key by checking its fingerprints. You can check the fingerprints found in the Instance Configuration section of your self-managed instance’s Help pages ( this Instance Configuration page shows an example).
Roles and permissions
CircleCI users have different abilities depending on assigned roles in a particular organization. For a detailed list of CircleCI org and project roles and associated permissions, see the Roles and permissions page.
User settings
Account integrations
In the User Settings section of your CircleCI user profile, you have the ability to enable multiple account integrations.
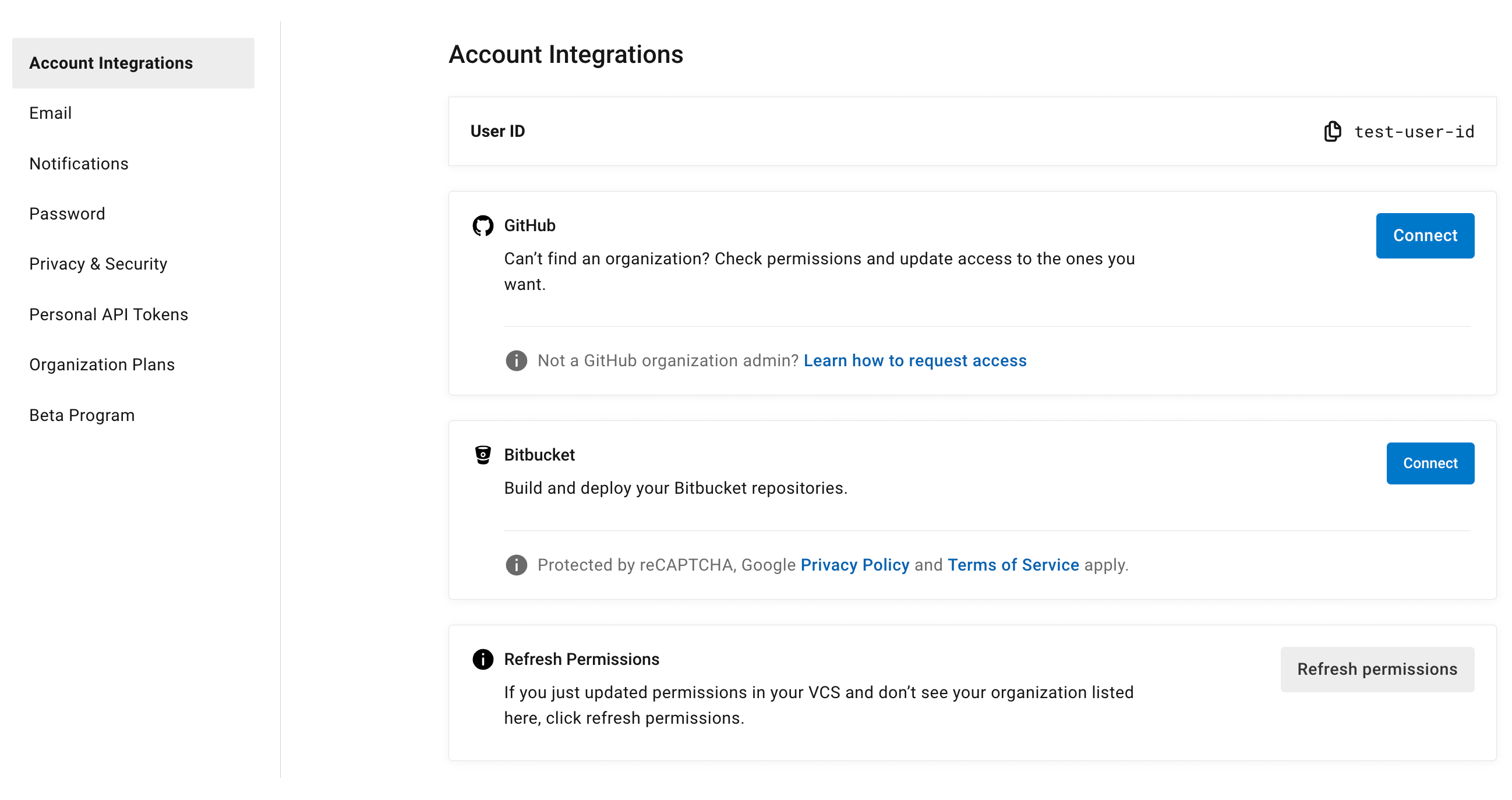
The ability to connect to multiple account integrations on CircleCI allows you to:
-
Access all source controls on your account.
-
Use all authentication methods available on CircleCI.
Deprecated system environment variables
A number of built-in environment variables are not available in GitLab-based projects. VCS support for each environment variable is indicated in the Built-in environment variables table on the Project values and variables page. If your pipelines need these environment variables, we recommend you use suitable replacements from the available pipeline values.
Coming soon
The following sections are features of CircleCI which are not currently fully supported for GitLab. These features are planned for future releases.
Account integrations
Currently, there is no method to manage the connection with GitLab outside of the project setup, trigger, and configuration settings. CircleCI is working on enabling users to manage their users’ GitLab identity as part of their user profile’s account integration settings.
Passing secrets to forked pull requests
Passing secrets to forked pull requests is not a currently supported option for GitLab integrations.
Scheduled pipelines
The ability to schedule pipelines is not currently supported for GitLab projects. This feature is planned for a future release.
Stop building
GitLab integrations do not currently support the Stop Building option that can normally be found in Project settings. The recommendation is to delete your webhooks in your GitLab repository if you no longer want a CircleCI pipeline to run.
Additional SSH keys only
Deploy keys and user keys are not used by GitLab integrations. GitLab keys are stored in Project Settings > Additional SSH Keys. However, CircleCI does not recommend manually managing your SSH keys for code checkout. Instead, use the Set Up Project option, or Project Settings > Configuration, to maintain connections to your repository.
Free and open source setting
Open source plans are not currently available to GitLab customers. CircleCI will keep the open source community up to date as work continues to support this.
Test Insights
Test Insights is currently not supported for GitLab customers.
CircleCI self-hosted server product
GitLab is not yet supported for CircleCI server.